What is DNS filtering
DNS filtering, or Domain Name System filtering, is a cybersecurity mechanism designed to control and restrict access to websites and online content based on predefined criteria, including blocking malware, social media websites, restricting access to web content, and prohibiting access to prohibited websites. It plays a pivotal role in safeguarding networks and internet users against a plethora of online threats, including phishing links and malicious software. It operates at the DNS level, intercepting domain name resolution requests made by your devices when you attempt to access a website. DNS filtering systems analyze these requests and determine whether the requested website or web server should be allowed or blocked based on established policies.
What does DNS stand for?
DNS, often referred to as the internet's phone book, plays a crucial role in translating user-friendly domain names into machine-readable IP addresses and DNS servers. In the context of DNS filtering, comprehending the intricacies of DNS is essential, as it forms the foundation of this powerful tool. DNS filtering is a method employed to control and enhance internet access by selectively blocking or allowing access to specific websites or content categories. To grasp the significance of DNS filtering, it is essential to delve into the core of DNS itself, as it serves as the gateway through which internet requests are processed and filtered, ensuring a safer and more secure online experience.
How Does DNS Filtering Work?
To answer the question 'What is DNS filtering' we have to explain how DNS filtering works. DNS filtering operates as a gatekeeper between your device and the internet. When you enter a website's URL in your web browser, your device sends a DNS query to a DNS server or DNS resolver to translate the domain name (e.g., https://google.com) into a unique IP address (e.g., 142.251.1.102). This (Internet Protocol) IP address is then used to connect to the website's server.
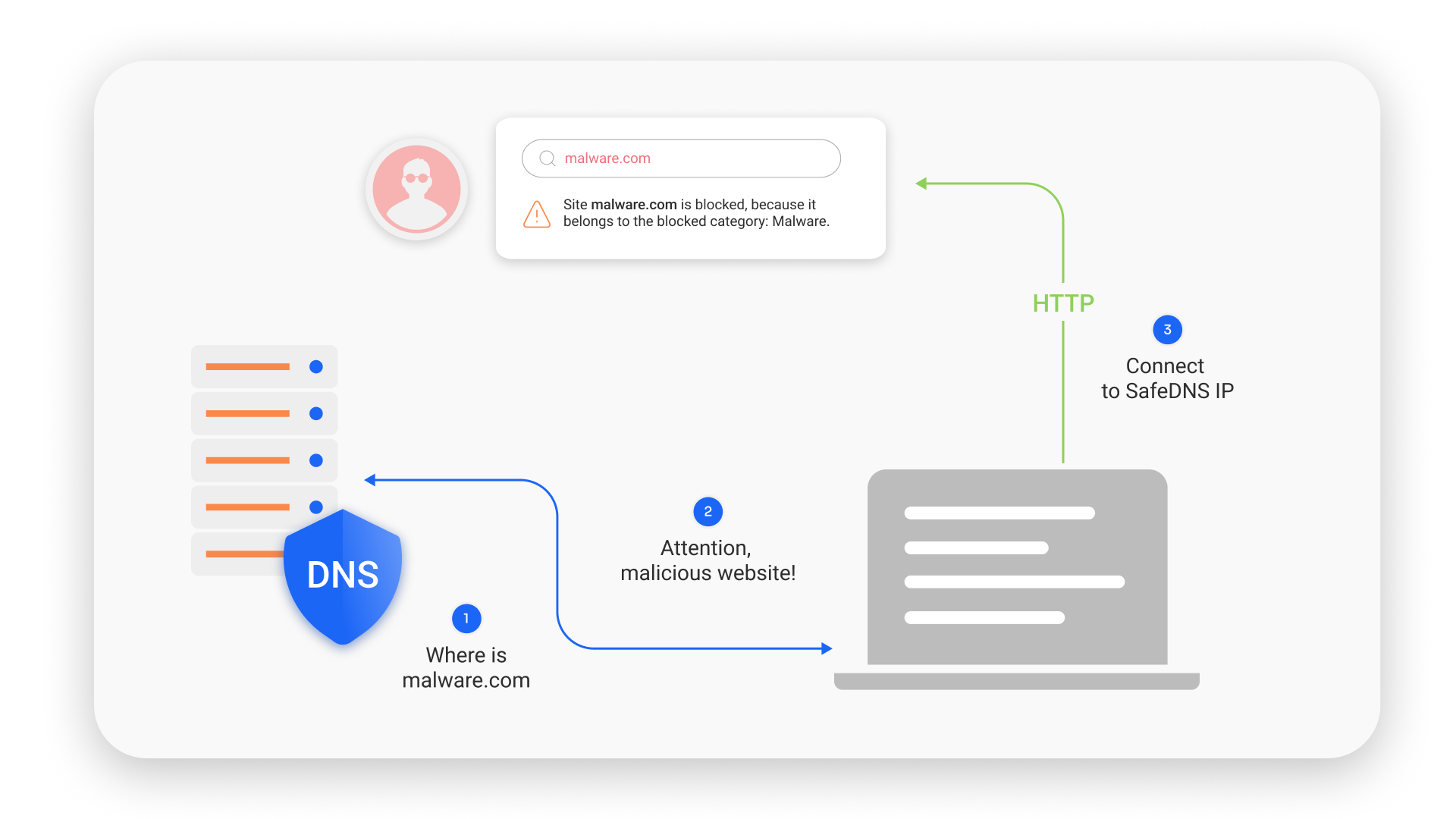
DNS filtering steps in during this process by redirecting DNS requests through a filtering system. The filtering system evaluates the requested domain against a predefined list of allowed or blocked websites, categories, or specific criteria. If the domain is on the allowed list, the DNS filtering system proceeds to resolve the domain and provide the corresponding IP address. If the domain is on the blocked list or violates specific criteria, the DNS filtering solution prevents the resolution, effectively blocking access to the website.
The Importance of DNS Filtering
Having a DNS filtering solution is a critical component of internet security and offers several important benefits:
Online Threats Protection: DNS filters can prevent user devices from access to websites hosting malicious content, including malware, ransomware, and phishing pages. By blocking access to these malicious sites, it helps protect your devices and data from cyber threats.
Content Control: DNS filtering allows organizations to enforce content restrictions. It can be used to block access to inappropriate, non-work-related or harmful websites, ensuring a safe and productive online environment.
Compliance and Data Protection: Organizations can use Domain Name System (DNS) filtering to enforce compliance with industry regulations and data protection laws. It ensures that sensitive information is not leaked or accessed from unauthorized sources.
Domain Name System (DNS) Filtering Techniques
DNS filtering employs various techniques to achieve its goals:
- Denylisting: This technique maintains a list of known malicious or undesirable domains and blocks access to them.
- Allowlisting: Conversely, whitelisting maintains a list of trusted domains and only allows access to those domains while blocking everything else.
- Category-Based Filtering: DNS filtering systems categorize websites based on their content, allowing administrators to block a malicious site or entire categories such as gambling, social media, or adult content.
- Custom Policies: Administrators can create custom policies to block or allow specific websites or content based on their organization's unique requirements.
DNS Filtering in Different Settings
DNS filtering finds application in various settings, each with its unique requirements and challenges:
Educational Institutions
Educational institutions often employ Domain Name System (DNS) filtering to restrict access to non-educational content and unwanted domains during school hours. This helps in maintaining a focused learning environment and ensures that students are not distracted by social media, gaming, or other unrelated websites.
Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
Small and medium-sized businesses can use DNS filtering to enhance cybersecurity. By blocking access to malicious websites, they can protect their networks from malware and phishing attacks. DNS filtering also helps in enforcing acceptable use policies and optimizing bandwidth.
Large Enterprises
Large enterprises have more complex needs when it comes to DNS filtering. They often require advanced filtering capabilities to manage a wide range of websites and content categories. DNS filtering in large enterprises is crucial for data protection, compliance, and ensuring employee productivity.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
ISPs can use DNS filtering tools to provide an added layer of security to their customers. By blocking access to known malicious domains, ISPs can protect their users from online threats and enhance their overall service quality.
DNS Filtering vs. Web Filtering
Web filtering is a comprehensive term that encompasses a variety of techniques for managing and controlling web traffic. DNS filtering, along with URL filtering, keyword filtering, and content filtering, is one of these methods. While DNS filtering focuses on evaluating and blocking or allowing websites based on their domain names, URL filtering assesses web addresses, keyword filtering screens for specific terms, and content filtering scrutinizes the actual content of web pages and internet traffic. These diverse web filtering methods offer organizations flexibility in tailoring their internet access policies and cybersecurity strategies to meet their specific needs.
Conclusion
DNS filtering is a powerful tool for managing and securing your online experience. Whether you're an ISP looking to comply with regulations or a business owner safeguarding your network from cyber threats, Domain Name System (DNS) filtering offers a flexible and effective solution for your DNS security strategy.
By understanding its workings and considering the challenges and considerations, you can make informed decisions about implementing DNS filtering in your specific context, ultimately enhancing your cybersecurity posture and protecting internet users from a multitude of threats, including malicious software and other DNS servers.
Take advantage of the SafeDNS trial period and try all the best features

