
DNS Threats: Vulnerabilities, Attacks, and Prevention Strategies
The Domain Name System (DNS) is crucial for internet functionality, acting as an address book that maps web addresses to their numerical IP addresses. However, DNS is also a vector for various cyber threats due to its foundational role in network communications. Malware, ransomware, phishing, and more sophisticated forms of cyberattacks like Domain Generation Algorithms (DGA) and DNS tunneling exploit DNS to infiltrate and damage systems.
142.250.189.206 - google.com
DNS security is an underrated risk. The technology is structured in a way that allows DNS packets to flow through the network without prior scrutiny. Moreover, DNS activity within networks is rarely monitored, creating a blind spot in cybersecurity. This oversight is significant, as 88% of companies suffer from DNS attacks every year, according to a 2023 report by EfficientIP. Despite the high risk, one-third of these attacks could be prevented at the DNS level, as highlighted by a 2023 study by Cisco.
What is inside DNS traffic
DNS traffic can carry a variety of parameters that play an important role in the exchange of information between clients and DNS servers. These parameters may include the type of request, the server’s response code, TTL (time to live of the record in the cache), transaction identifier, query options, etc. DNS queries are essential components of DNS traffic, involving requests made by clients to DNS servers to resolve domain names into IP addresses.
Moreover, DNS traffic can carry data about the IP addresses of DNS servers, information about network traffic, the location and configuration of domains, as well as much more that helps ensure the efficient operation of the Internet and its security. The DNS resolver plays a crucial role in processing these DNS queries, facilitating the exchange of information between clients and DNS servers. Here is a list of the main parameters:

Threats at the DNS level
Malware
Malicious software, or malware, includes various cyber threats such as viruses, trojans, spyware, adware, and techniques like DNS cache poisoning, where malware redirects users to malicious sites by exploiting DNS vulnerabilities. It can cause significant issues, from minor annoyances to major financial losses, by altering browser settings, using up computing resources, and collecting sensitive user data like passwords and credit card numbers.
DNS protection is crucial in combating malware by:
- Blocking access to malicious domains to prevent malware communication and data breaches.
- Monitoring for abnormal behavior to detect malware presence.
- Providing network activity logs to enhance incident response and mitigate security breaches quickly.
Ransomware
Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts a computer's files, rendering them inaccessible, and may lead to data breaches. The malware demands ransom for decryption, impacting both individuals and business operations.
DNS protection aids against ransomware by:
- Blocking access to ransomware's command and control servers to disrupt its communication.
- Preventing devices from connecting to malicious websites and email attachments that could initiate an attack.
- Enabling rapid, automated threat detection and alerts, facilitating a swift response to potential ransomware activity.
Phishing and Typosquatting
Phishing and Typosquatting are forms of cyber deception aimed at stealing sensitive information through fake websites and misspelled domain names. DNS spoofing is another method where attackers manipulate DNS records to redirect users to fraudulent sites, often for malicious purposes such as phishing, malware distribution, or denial-of-service attacks. These practices can compromise personal and corporate security, leading to financial losses and reputational damage.
DNS protection helps combat these threats by:
- Preventing access to fake websites designed to mimic legitimate ones, safeguarding user credentials.
- Utilizing algorithms to identify and block deceitful domains that resemble legitimate sites, protecting users from fraud.
Botnet, Cryptojacking, and C2C
Botnets, composed of internet-connected devices infected with malware, can perform various malicious activities, including DDoS attacks, data theft, and illegal cryptocurrency mining, leading to energy and productivity loss and potential financial and reputational damages. Botnets and C&C servers often utilize DNS requests to communicate and control compromised devices, highlighting the need for robust DNS protection strategies.
DNS protection helps by:
- Blocking access to known command and control (C&C) servers to disrupt botnet communications.
- Detecting and preventing connections to suspicious domains associated with botnets or C&C servers.
- Identifying unusual patterns that may indicate botnet presence to prevent system infections.
Parked Domains
These are domain registrations on DNS servers offering parking services, not actively used but may host illegitimate content at a remote server at any time. SafeDNS implements a verification pipeline using real-time data from various sources to monitor new domains and their content, identifying and filtering out illegitimate resources at an early stage. The system establishes domain-IP-autonomous system (AS) relationships, which helps in the early detection of malicious domains.
DGA and DNS Tunneling Attacks
DGAs create numerous domain lists to maintain botnet communication and evade security measures. They don’t directly harm networks but enable the infiltration of malicious software and impede its removal, potentially resulting in corporate network damage.
DNS protection contributes by:
- Detecting and blocking DGA-generated domains using machine learning and traffic analysis, ensuring queries are directed to the correct IP address by verifying information with the authoritative DNS server.
- Monitoring and obstructing abnormal DNS activity that could signify DNS tunneling.
- Maintaining a database of known DNS tunnels to block unauthorized connections and data transmission.
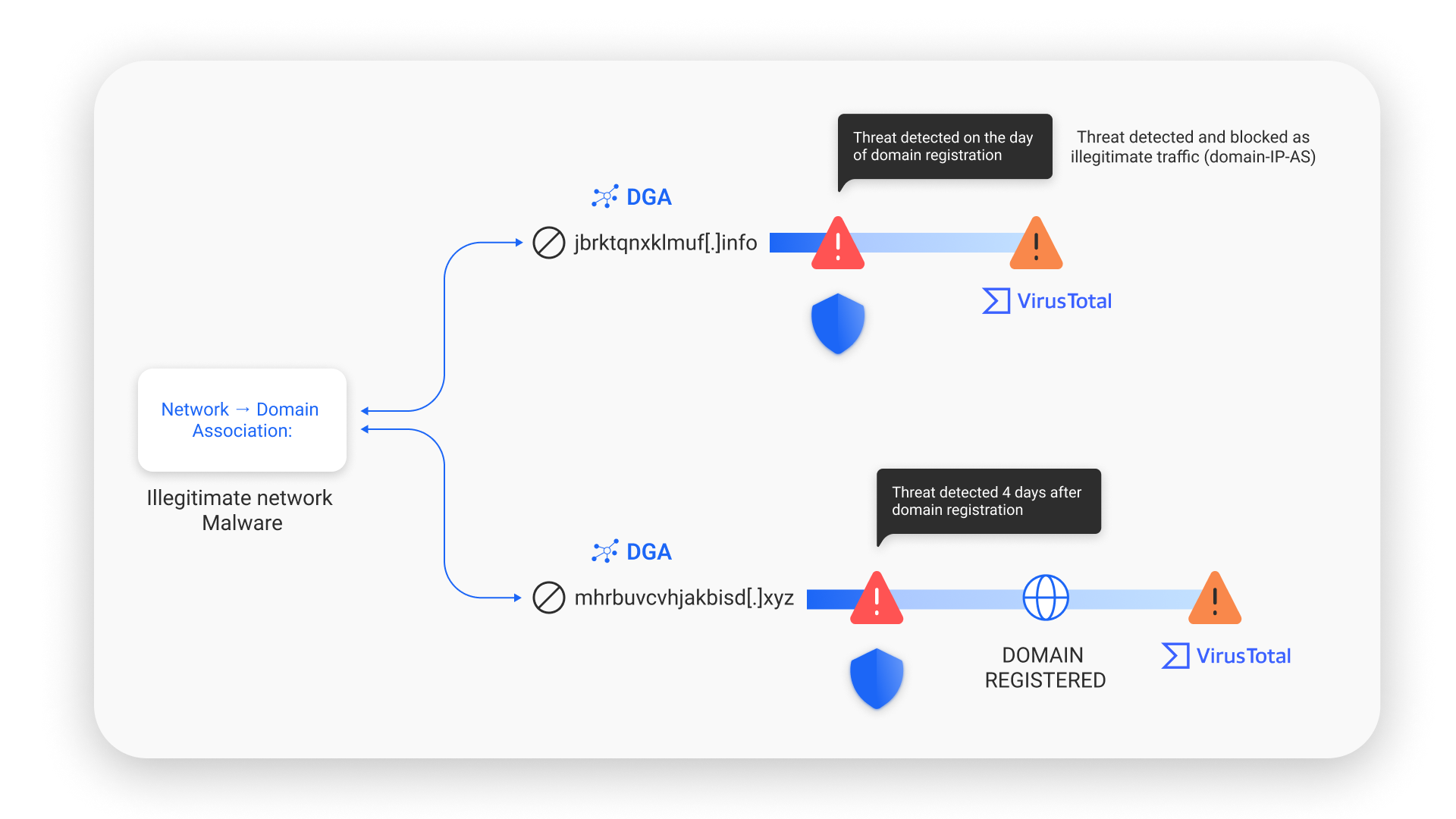
An authoritative DNS server plays a crucial role in this process by holding the official and up-to-date information about a domain name's IP address, ensuring that DNS queries are resolved with the correct IP address, which is essential for preventing DNS tunneling and DGA threats.
Threats at the DNS level are a major concern because they can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and damage reputations. However, with the right solutions in place, many of these threats are preventable. SafeDNS is at the forefront of this defense, leveraging the latest advances in AI and machine learning to effectively detect and mitigate threats.
By processing billions of queries every day, SafeDNS provides real-time monitoring and proactive measures to secure networks. The power of SafeDNS lies in its extensive categorization database of over 2 billion URL records, providing unparalleled protection. This comprehensive approach ensures that SafeDNS not only identifies existing threats, but also anticipates emerging ones, providing a robust shield against DNS-level threats. With SafeDNS, organizations can secure their online presence and ensure the continuity and integrity of their digital assets.
Take advantage of the SafeDNS trial period and try all the best features

